Identifying a fake image online can be challenging as technology has made it easier to manipulate images. In a blog post from 2020, titled “OSINT Research & False Positives” we discussed how easy it was to create a computer generated image. However, fast forward to 2023, with the explosion of artificial intelligence, creating computer generated images of all kinds have taken on a life of their own.
Taking a closer look at examples of fake images can help to train your eye to look for certain traits of the image to determine it’s legitimacy. Nothing is infallible of course, but there are some steps you can take to assist in identifying fake images. In fact, next time you have some time to kill, check out “Which Face is Real” to test out your knowledge!
Signs of computer-generated manipulation
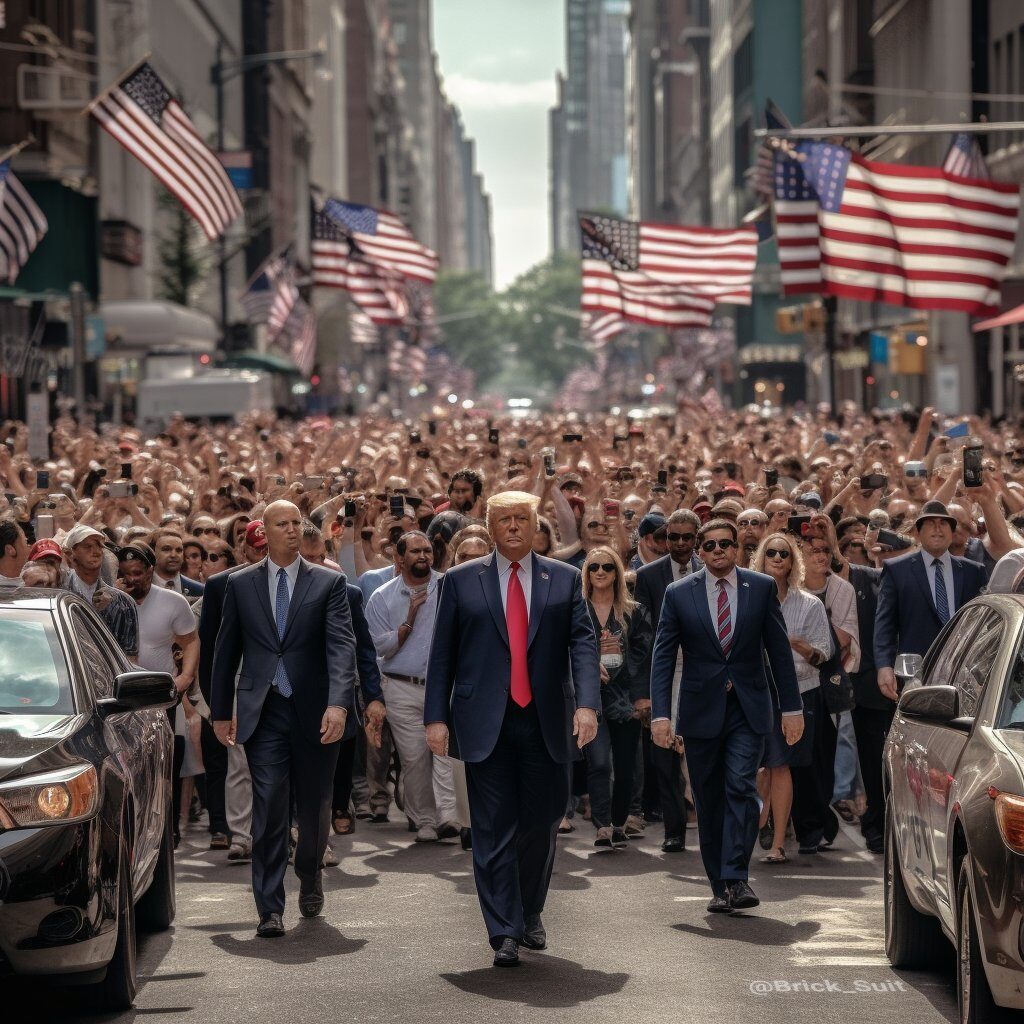
The photo above was identified as fake through Snopes.com’s fact checking. The photo was posted to a Twitter user’s feed. Snopes is a great resource for debunking fake profiles, images and news. According to the article on the site, “The photo was generated by artificial intelligence (AI), with several telltale signs of computer-generated manipulation. For examples, an area near Trump’s lower lip showed another trace of lip; the faces of the presumed Secret Service agents and many crowd members were disfigured; some heads looked more like skulls, and the flags’ coloring wasn’t consistent. Additionally, the man immediately behind Trump not only had signs of digital doctoring in his face but also his right hand.”
The photo was fake; it was not a genuine documentation of Trump arriving to New York for his booking and arraignment. The Twitter user acknowledged that fact, writing in a reply tweet, “I didn’t find this [photo]. I generated it via prompts.”
Source: Snopes.com
Systems such as Stable Diffusion, DALL-E, and Midjourney make it easy for anyone to create images to fit their narrative. The good news is that historically, AI generated systems have struggled to mimic human hands as an example. Something to keep in mind, for now at least.
Scientific American’s recent article on Artificial Intelligence, states that the some AI images are so hard to detect that it may take AI to identify it as being a fake!
“It’s pretty amazing, in terms of what AI image generators are able to do,” says S. Shyam Sundar, a researcher at Pennsylvania State University who studies the psychological impacts of media technologies. “There’s been a giant leap in the last year or so in terms of image-generation abilities.”
Tips to Identifying Fake Images Online
- Look for inconsistencies: Study the photo carefully for inconsistencies or irregularities in the image. Look for blurred edges, mismatched shadows, or disproportionate objects. These inconsistencies can be a sign of photo manipulation.
- Check the metadata: Most digital photos contain metadata that includes information such as the date, time, and location of the photo. Check this information to ensure it is consistent with the photo’s content.
- Reverse image search: Use a reverse image search tool like Google Images, Bing Images, Yandex Images or TinEye to check if the photo has been used elsewhere on the internet. If it has been used in different contexts, it may be a sign that it’s a fake.
- Consult experts: If you’re still unsure about the authenticity of a photo, consult experts such as photo forensics specialists, journalists, or fact-checking organizations.
- Be skeptical: Finally, always approach photos online with a healthy dose of skepticism. Be wary of photos that seem too good to be true or those that are designed to elicit an emotional response.
- Look for a Watermark: DALL-E 2 places a watermark on every photo generated through their system. The Watermark is shown below (the color bar). It is placed very small on the image. It can be removed however, so it will not always be shown.
By following these steps, you can increase your chances of identifying a fake photo online.

