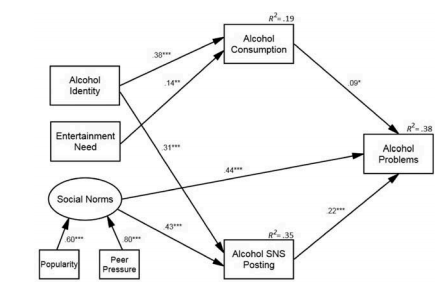
Educating teens on social media use and responsibility is quite the challenge – with the immediacy and constant availability of social media, teens tend to use social media to vent frustration, share conflict, or even sometimes with the intent to harm a classmate’s reputation. Most times, teens don’t have malicious intent – they are simply posting their thoughts to social sites because that’s what they know.
In Alberta, they are taking a more focused approach to taking social media content offline to resolve content and education both parents and students. As they realizing that most social media postings and conflict are not necessarily criminal in nature, but need to be addressed, they have focused on intervention techniques that take the social conflict offline for resolution.
The RCMP, who is heading up this initiative, does not (yet) monitor social media to identify such content; instead, they rely on parent and student reports of content that is deemed problematic. From there, they formed a community justice forum which brings teens (and parents) together to discuss issues raised online. A recent article sums up teen social media conflict quite nicely:
“A lot of the issues are interpersonal conflict being dealt with in an inappropriate way,” says Kading. “Even as adults we are learning socialization skills all the time. I think a lot of the time, the conversations (our officers have) on an informal basis with young people can serve more effectively than if we have to go a formal route.”
Schools can learn from this example and even take a more proactive approach through social media monitoring. While it’s almost impossible to capture any and all conflict, location based monitoring can help monitor social media content that is posted while within the school boundaries. By identifying potential issues, schools can proactively engage at risk students or address student conflicts as they arise. This can help educate students on the reality and permanent nature of online content, and make them think before they post. The schools can provide students with tools for handling conflict offline, thus building relationship skills among their student body.
While this will always exist, finding ways to education the teenage set on social media responsibility and offline interpersonal relationships can be effective in raising responsible young adults.